Release time:2024年4月25日
Author:Kama
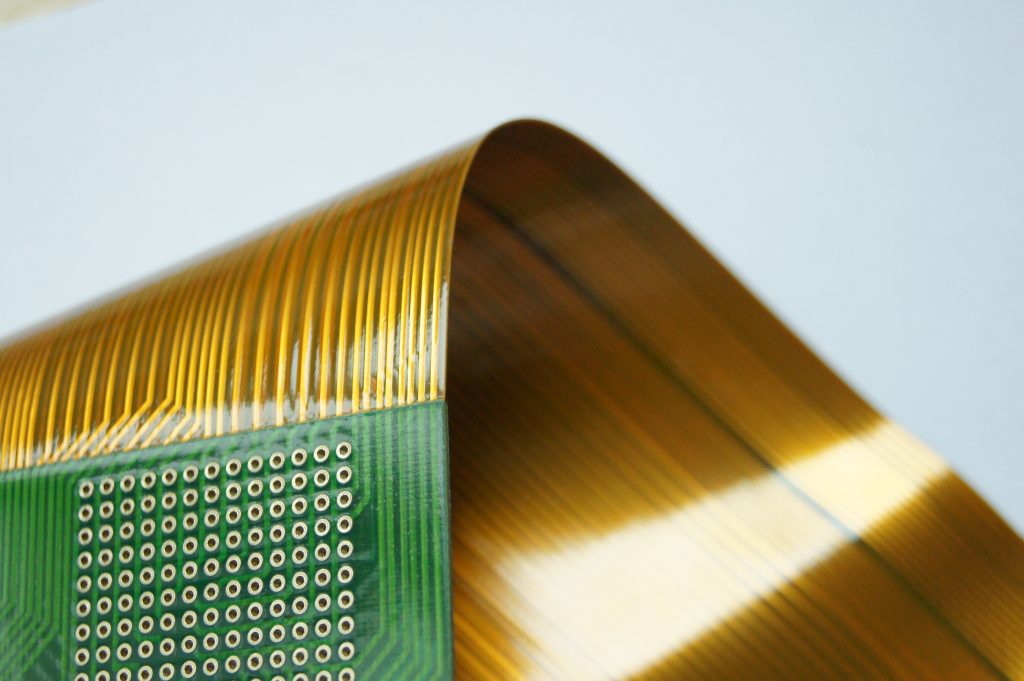
Flexible or Flex PCBs are also called flex circuits and can be fully bent to a specific shape.
Rigid PCBs consist solely of rigid materials and are not designed to bend or flex.
A Rigid-Flex PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is a type of circuit board that combines elements of both rigid and flexible PCBs into a single structure.
In a Rigid-Flex PCB, sections of rigid and flexible substrates are combined to create a single board. This allows the PCB to bend or flex at specific points while maintaining rigidity in other areas. The rigid sections typically contain components and provide mechanical support, while the flexible sections allow the board to conform to the shape of the device it's installed in or to accommodate movement in applications such as wearable devices, foldable electronics, or compact electronic devices.
| Advantages | Description |
| Mechanical Stability | Rigid PCBs provide a stable platform for mounting electronic components. They maintain their shape and structure, ensuring consistent performance even under mechanical stress. |
| High Component Density | Rigid PCBs allow for densely populated designs, meaning more electronic components can be mounted on a single board. This is essential for miniaturization and compact electronic devices. |
| Improved Heat Dissipation | Rigid PCBs typically have better heat dissipation properties compared to flexible PCBs, as they can be designed with thicker copper layers and incorporate heat sinks or thermal vias to efficiently dissipate heat generated by electronic components. |
| Enhanced Electrical Performance | Rigid PCBs offer excellent electrical performance, with consistent impedance characteristics and minimal signal distortion. This makes them suitable for high-speed and high-frequency applications. |
1.Mechanical Stability: Rigid PCBs provide a stable platform for mounting electronic components. They maintain their shape and structure, ensuring consistent performance even under mechanical stress.
2.High Component Density: Rigid PCBs allow for densely populated designs, meaning more electronic components can be mounted on a single board. This is essential for miniaturization and compact electronic devices.
3.Improved Heat Dissipation: Rigid PCBs typically have better heat dissipation properties compared to flexible PCBs, as they can be designed with thicker copper layers and incorporate heat sinks or thermal vias to efficiently dissipate heat generated by electronic components.
4.Enhanced Electrical Performance: Rigid PCBs offer excellent electrical performance, with consistent impedance characteristics and minimal signal distortion. This makes them suitable for high-speed and high-frequency applications.
1.Flexibility: As the name suggests, flex PCBs are highly flexible, allowing them to bend and twist without damaging the circuitry. This flexibility makes them ideal for applications where traditional rigid PCBs cannot be used due to space constraints or the need for bending.
2.Space-saving: Flex PCBs are thinner and lighter than traditional rigid PCBs, making them ideal for compact electronic devices where space is limited. They can be designed to fit into tight spaces or conform to the shape of the device housing, maximizing the use of available space.
3.Reliability: Flex PCBs offer improved reliability compared to rigid PCBs in many applications. Their ability to withstand bending, vibration, and shock makes them less prone to mechanical failures. Additionally, flex PCBs have fewer solder joints and interconnects, reducing the risk of failure due to solder fatigue or connection issues.
Improved thermal management: Flex PCBs can dissipate heat more effectively than rigid PCBs, thanks to their thinner profile and ability to conform to heat sinks or other cooling mechanisms. This can help prevent overheating and prolong the lifespan of electronic components.

Cost Savings: While the initial cost of rigid-flex PCBs may be higher than traditional rigid PCBs, the overall cost of manufacturing and assembly can be lower due to reduced material usage, simplified assembly processes, and lower maintenance and repair costs over the product's lifecycle.
Improved Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Rigid-flex PCBs can be designed to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) by carefully controlling signal traces and grounding planes. This is particularly important in high-frequency and high-speed applications where EMI can degrade system performance or cause malfunctions.
Streamlined Assembly: Integration of rigid and flexible substrates into a single design reduces the number of interconnections and assembly steps, simplifying the manufacturing process and reducing assembly time and costs.
Miniaturization: Rigid-flex PCBs enable the miniaturization of electronic devices by eliminating the need for bulky connectors and cables. This is particularly advantageous in portable and wearable electronics, where size and weight are critical factors.
In the ever-evolving landscape of electronic design, rigid-flex PCBs have emerged as a versatile solution that bridges the gap between traditional rigid and flex PCB technologies. By combining the mechanical stability of rigid boards with the flexibility of flexible substrates, rigid-flex PCBs offer designers unparalleled freedom in creating compact, reliable, and high-performance electronic assemblies. While they may entail higher costs and complexity in manufacturing, the benefits they provide in terms of space savings, reliability, and design flexibility make them a compelling choice for a wide range of applications. As technology continues to advance, rigid-flex PCBs are likely to play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of electronics.